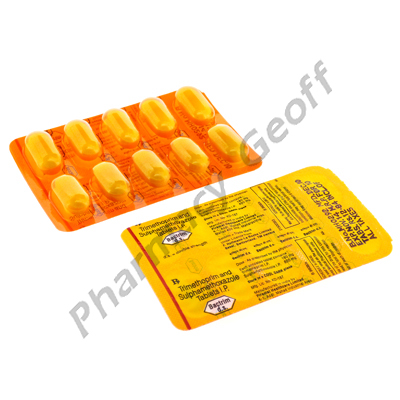
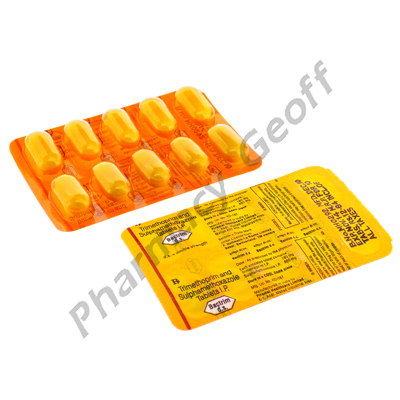
Bactrim DS (Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole) - 160mg/800mg (10 Tablet)
Bactrim DS contains two different antibiotics - trimethoprim (160mg) and sulfamethoxazole (800mg). This combination is also called Co-trimoxazole. It is used to stop the growth of bacteria that are causing infection. Bactrim is used primarily in the treatment of urinary tract infections (UTIs), upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) and lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs) and bowel infections.
Bactrim DS Warnings and Precautions
Do not take Bactrim DS (Co-trimoxazole) is you have any of the follwing:
- sever liver or kidney disease
- anaemia (low red blood cell count)
- leukopenia (low white blood cell count)
- low platelet count
- any other serious blood disorder
Tell your doctor or all medicines you are currently taking as well as any allergies you have, especially to any antibiotics.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, or if you a breast-feeding or planning to breast-feed.
How to take Bactrim DS
Bactrim DS comes as a tablet. Each strip contains 10 tablets.
In most cases, the recommended dose is two tablets taken twice daily for a period of at least five days.
Your doctor will tell you exactly how much Bactrim DS to take and how long to take it for.
Bactrim DS Side Effects
Most side effects of Bactrim DS are mild and temporary. The most common side effects are:
- Feeling sick, vomiting, stomach upset, diarrhoea
- Oral thrush (white, furry sore tongue and mouth)
- Vaginal thrush (sore and itchy vagina, vaginal discharge)
- Headache
- Dizziness or feeling unsteady
- Muscle or joint aches
- Increased sensitivity to sunlight
Serious side effects occur less frequently, but can require urgent medical attention. Contact your doctor or emergency department if you notice:
- Any skin reaction, redness, itching, swelling or blistering of the skin (e.g. skin rash, 'hives', spots, or blisters)
- Swelling of the face, lips or tongue
- Sore mouth or sore eyes
- Red and swollen eyes
- Blurred vision
- A high temperature (fever)
- Yellowing of the eyes or skin (jaundice)
- Passing very little or no urine
- Seizures or fits
- Watery and severe diarrhoea, which may also be bloody
- Severe stomach cramps
- Unusual tiredness or weakness and looking pale
- Bruising or bleeding more easily than normal
- Signs of frequent infections such as fever, chills, sore throat or mouth ulcers
- Severe and persistent headache
- Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet
- Cough, shortness of breath
|